- Details
- Written by: Mahdi
- Category: Research Groups
- Hits: 163
Machine Learning with Python
Learn the foundations and practice of Machine Learning using Python through a structured, hands-on program. In this course you’ll move from data handling to building and evaluating real ML models, and finish with a complete end-to-end project you can showcase.
What You Will Learn
-
Python for ML: Write clean, reproducible code and work efficiently with notebooks (Jupyter) and virtual environments.
-
Numerical computing with NumPy: Vectors, matrices, broadcasting, and performance tips for fast computation.
-
Data wrangling with Pandas: Import, clean, transform, and join real-world datasets; handle missing values and outliers.
-
Data visualization with Matplotlib: Communicate insights with clear charts and plots; best practices for readable visuals.
-
Supervised learning – Regression: Train, validate, and tune models (Linear/Polynomial Regression, Regularization, Metrics).
-
Supervised learning – Classification: Build and compare classifiers (k-NN, Logistic Regression, Decision Trees, SVM); confusion matrix & ROC-AUC.
-
Model selection & evaluation: Train/validation/test splits, cross-validation, overfitting vs. underfitting, feature scaling, pipelines.
-
Final project implementation: Build a complete ML solution—from data ingestion and EDA to a production-style notebook with results and report.
Why Take This Course?
Gain practical, industry-relevant skills to analyze data and ship ML solutions. Learn by doing with guided coding, mini-assignments, and a capstone project so you can apply your skills immediately at work or in future studies. You will develop problem-solving and debugging habits essential for real projects and receive focused mentorship from an instructor with academic and industrial background.
Course Syllabus
-
Python Basics for Machine Learning (syntax, notebooks, environments)
-
NumPy Fundamentals (arrays, broadcasting, performance)
-
Pandas for Data Handling (cleaning, joins, grouping)
-
Data Visualization with Matplotlib (EDA & storytelling)
-
Regression Algorithms (linear, regularization, metrics)
-
Classification Algorithms (k-NN, logistic, trees, SVM; evaluation)
-
Final Project (end-to-end ML pipeline + report)
Each module includes live coding, short exercises, and a real-world mini-dataset. The final session is dedicated to project review and feedback.
What You’ll Achieve
-
Confidence working with real-world datasets and messy data.
-
Ability to implement core ML algorithms in Python using NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, scikit-learn.
-
Skills to evaluate models properly and improve accuracy with sound methodology.
-
A complete ML project to showcase in your resume, portfolio, or applications.
Course Information
Instructor: Mohsen Zaker (Computer Engineer & ML Instructor, AICER Lab)
Duration: 16 hours
Start Date: 4 Mehr 1404
Certificate: AICER Lab completion certificate
👉 Register now and bring your ML ideas to life!
- Details
- Written by: Mahdi
- Category: Research Groups
- Hits: 150

Arduino & AVR Microcontroller (20 Hours)
Learn Arduino and AVR programming from scratch and build exciting automation and IoT projects. Arduino and AVR are some of the most popular microcontrollers for beginners, makers, and professionals alike. They are widely used in DIY electronics, automation systems, and even industrial prototypes.
This course will guide you from setting up your first Arduino board to building complete hardware projects. By the end, you will not only write Arduino code but also connect and control sensors, actuators, and communication modules.
Key topics covered:
- Introduction to Arduino and AVR microcontrollers
- Basics of embedded C programming
- Working with sensors for automation and data collection
- Controlling actuators (motors, relays, LEDs, etc.)
- Implementation of automation systems
- Communication using I2C, SPI, and UART
- Integrating RFID systems for identification and security
- Final project combining all the learned skills
Practical projects you will build:
- Smart home automation system (light/sensor control)
- Data logging using sensors
- Simple robotic control
- RFID-based security system
Who is this course for?
- Beginners with no prior experience in electronics
- Students starting microcontrollers before advanced systems
- Makers & hobbyists interested in DIY and prototyping
- Engineers who need quick proof-of-concept automation
Instructor: Ebrahim Saber (M.Sc. Mechatronics Engineering, Engineer at AICER Lab)
Duration: 20 hours (with hands-on practical exercises)
Start Date: September 10 (20 Shahrivar)
👉 Register now and start building amazing hardware projects with Arduino & AVR!
- Details
- Written by: Mahdi
- Category: Research Groups
- Hits: 169

STM32 Microcontroller Programming (24 Hours)
Learn to master ARM-based STM32 microcontrollers through a carefully structured, hands-on program.
This comprehensive 24-hour course takes you from the foundations of ARM architecture to the development of advanced embedded systems projects.
What You Will Learn:
- Introduction to ARM architecture: Understand the principles behind ARM-based processors and the STM32 family.
- C programming for embedded systems: Write efficient and optimized C code for hardware control.
- GPIO, UART, Timer, ADC, and Interrupts: Interface with the outside world, handle real-time signals, and manage hardware communication.
- Communication protocols: Use standard embedded communication systems to connect sensors and devices.
- Real project implementation: Build a complete project integrating multiple course concepts.
Why Take This Course?
- Gain practical, industry-relevant knowledge in embedded systems.
- Work directly with real STM32 hardware and see your code in action.
- Develop problem-solving and debugging skills essential for embedded developers.
- Receive mentorship from an expert with academic and industrial background.
Instructor: Ebrahim Saber (M.Sc. in Mechatronics Engineering, Engineer at AICER Lab)
Duration: 24 hours of intensive learning with hands-on projects
Start Date: September 10 (20 Shahrivar)
👉 Register now and bring your embedded ideas to life!
- Details
- Written by: Mahdi
- Category: Research Groups
- Hits: 336
Continuous monitoring of industrial equipment is one of the key needs of modern industries, as it helps detect early deviations and prevent costly breakdowns. Sound and vibration anomalies often appear as the first warning signs of mechanical or operational failures. However, many conventional monitoring systems are limited by low sampling rates, lack of real-time analysis, or the absence of remote monitoring, making them less effective in demanding industrial environments. Previous studies have explored different methods for anomaly detection. Some focused on sound signal analysis using statistical methods, while others employed vibration sensors to detect abnormal patterns. Although these approaches provided valuable insights, most relied on offline processing or low-power hardware with limited frequency analysis capabilities. In addition, the lack of integrated network connectivity often prevented real-time remote supervision, which is increasingly critical in today’s connected industries.
Our research addresses these challenges by introducing an integrated system that combines the ESP32 microcontroller, FFT-based frequency analysis, and TCP/IP network communication. The innovation lies in merging high sampling rates, real-time signal processing, and a dynamic remote monitoring interface. This design not only increases detection accuracy but also allows flexible integration with various industrial devices, ensuring broader applicability across different sectors.
Initial experiments show that the proposed system can detect anomalies quickly and with high accuracy under diverse operating conditions. These results highlight the potential of our solution to enhance equipment performance, reduce maintenance costs, and prevent unexpected production stops. By bridging the gap between traditional monitoring methods and modern industrial needs, this system provides a practical, cost-effective, and scalable tool for ensuring reliability and safety in industrial operations.

The proposed system is built around three main components: hardware, software, and network connectivity. On the hardware side, sound and vibration data are collected by sensors and processed in real time using the ESP32 microcontroller. Frequency analysis is performed directly on the device through the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm, ensuring that anomalies can be detected quickly and efficiently without the need for heavy external hardware.
The processed results are then sent to a Python-based software interface, where the data is displayed and statistically analyzed to identify abnormal patterns. Finally, through the TCP/IP protocol, this information is transmitted to a web-based monitoring service, enabling remote supervision anytime and anywhere. By combining data acquisition, real-time processing, and online accessibility, the system provides a robust and scalable solution for modern industrial environments.
Hardware
The system uses an ESP32 microcontroller with sound and vibration sensors to capture data at high sampling rates. The KS-07S microphone records audio signals, while the ADXL335 accelerometer tracks vibrations, with interface circuits filtering out noise for clean analysis.Lightweight software on the ESP32 processes the signals using FFT and vibration intensity calculations, then sends the results to a Python-based interface. This setup makes it possible to detect and display sound and vibration anomalies in real time, with the added benefit of remote monitoring via network connection.
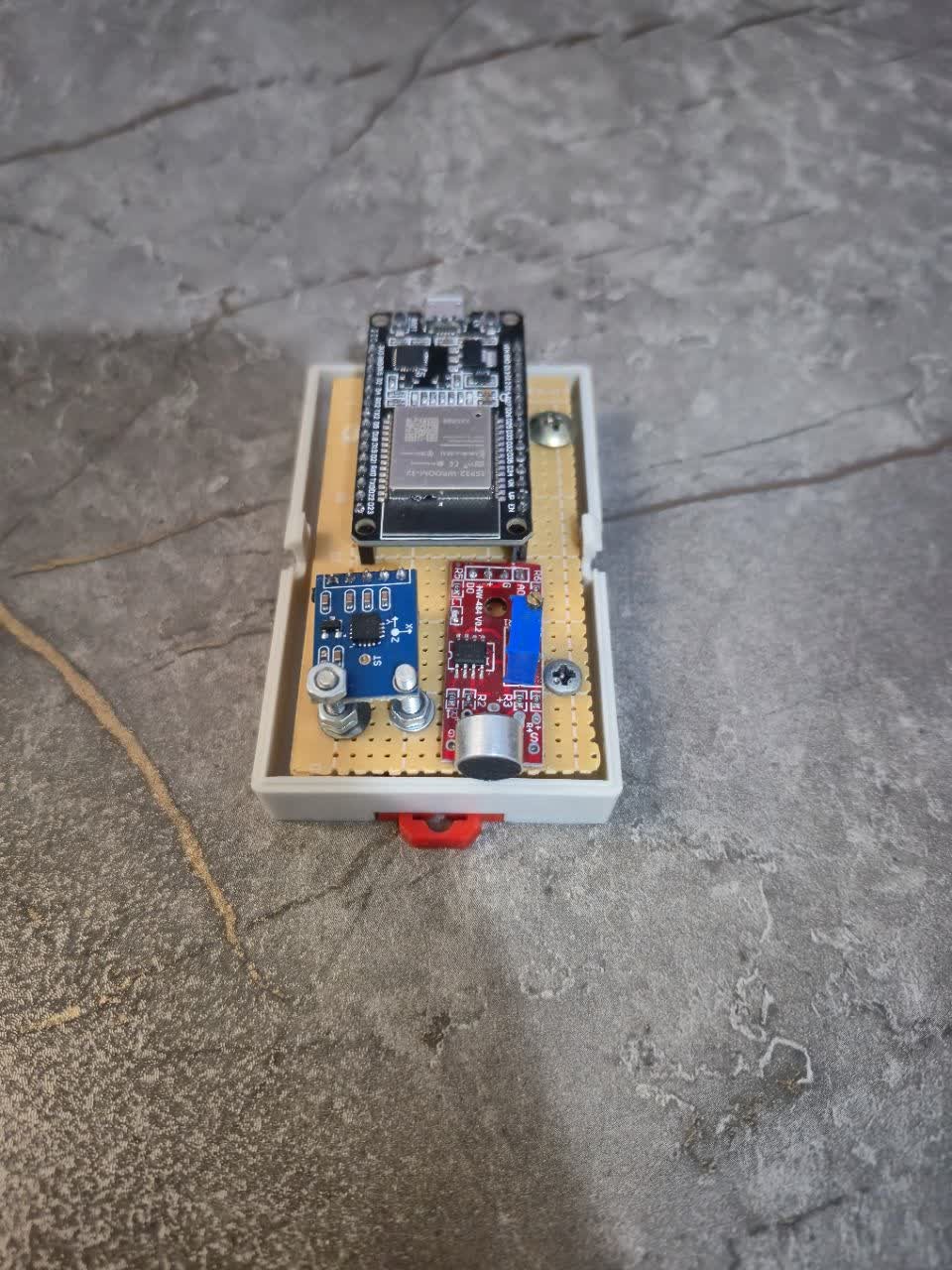
User Interface Software
The user interface was developed in Python using libraries such as ttkbootstrap, matplotlib, and numpy. It provides real-time charts for sound and vibration signals, threshold controls, and zoom features, while anomalies are detected using a z-score method for audio and a fixed threshold for vibration. For remote monitoring, data is transmitted via TCP/IP using the ESP32 with an ENC28J60 network module, and received in JSON format by a web service that displays live dashboards and anomaly reports. Network latency was measured at less than 100 ms, ensuring real-time performance. System evaluation in both real and simulated conditions confirmed its accuracy in detecting anomalies, fast response times, and stable operation even under noisy environments.
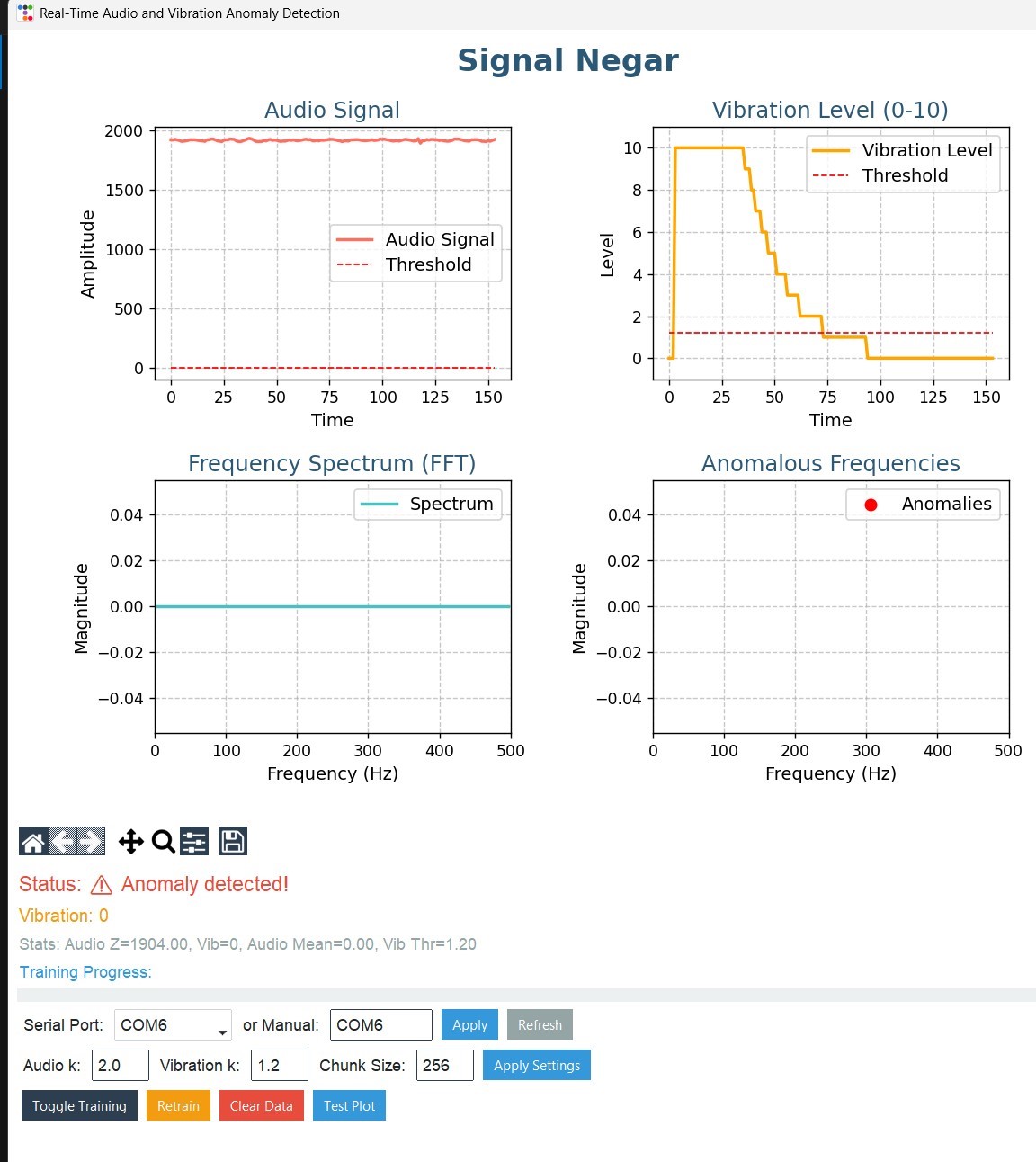
This study successfully developed an integrated system for real-time detection of sound and vibration anomalies in industrial equipment. The approach overcame common limitations of earlier solutions, such as offline processing, low sampling accuracy, and the lack of remote monitoring. Tests confirmed high accuracy in detecting anomalies, fast response times, and stable operation even under challenging and noisy conditions. These results underline the potential of the system to improve safety, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance efficiency in industrial environments.
At the same time, certain challenges remain, such as reduced accuracy in extremely noisy conditions and sensitivity limits for small-scale vibrations. Future research should aim to refine sensor accuracy, improve noise handling, and expand adaptability for diverse industrial applications. With these enhancements, the system can evolve into a reliable and scalable tool for smart factories, supporting safer, more efficient, and sustainable industrial operations.
Developed and researched by Alireza Maghsoudi – Aicer Lab
- Details
- Written by: Mahdi
- Category: Research Groups
- Hits: 401
Water, as the most vital resource for life, is increasingly threatened by chemical and environmental pollution. Traditional methods of water quality monitoring, while useful, are often costly, time-consuming, and limited in efficiency. To address these challenges, researchers have turned to innovative approaches such as biomonitoring—a technique that uses living organisms, especially fish, as sensitive indicators of environmental changes. In recent years, the integration of biomonitoring with modern technologies like image processing and machine vision has opened new horizons for real-time and accurate water quality assessment. This combination not only improves efficiency but also provides continuous, non-invasive, and highly sensitive monitoring, making it a promising solution for ensuring safe and sustainable water resources.
Global studies show big progress in using living organisms for water biomonitoring. Fish, daphnia, and other aquatic animals can act as early warning systems for pollution, showing changes in the environment before chemical tests can. But there are still many challenges, especially in bringing these systems to developing countries where equipment and expertise are limited.
Commercial platforms like FishToximeter and DaphniaToximeter work very well in laboratories and are highly accurate. However, they are expensive, need special conditions, and are hard to use outside controlled labs. They also depend on special hardware, private software, and expert operators, which makes them difficult to expand or use locally. To solve these issues, we need more affordable and flexible systems that can work in different environments and be easier to use in places with fewer resources.
The Aicer research team has developed an intelligent biomonitoring system named BIO AI. The main objective of this study is the design and implementation of an intelligent biomonitoring system based on the behavioral analysis of zebrafish, capable of detecting real-time changes in water quality and providing early warnings of potential pollutants. Using advanced machine vision algorithms, the system records and analyzes fish movements under both normal and contaminated conditions, enabling the identification of abnormal behavioral patterns caused by toxic substances. In addition to the visual monitoring module, the project also introduces an independent environmental control system built on the ESP32 microcontroller. This module continuously monitors and regulates aquarium conditions such as water temperature, level, flow rate, and aeration. It integrates a DS18B20 temperature sensor with a PID controller, a water level sensor for maintaining a fixed volume (8 liters), a YF-S201C flowmeter for real-time flow measurement, and a timer-controlled relay for aeration.
By combining behavioral image analysis with automated environmental control, the proposed system delivers a comprehensive and fully automated biomonitoring solution that can be applied in water treatment industries, aquaculture, environmental research, and water resource management.
System Schematic
The BIOAI – AICER201 biomonitoring system is designed as a fully integrated platform that brings together water flow, environmental controls, and intelligent monitoring. The schematic, visually demonstrates how the system creates and maintains healthy aquarium conditions while performing real-time behavioral analysis of zebrafish.
At its core, the diagram shows the smooth integration of hardware, sensors, and software interfaces—working together to manage water quality with precision and to detect early signs of pollutants.
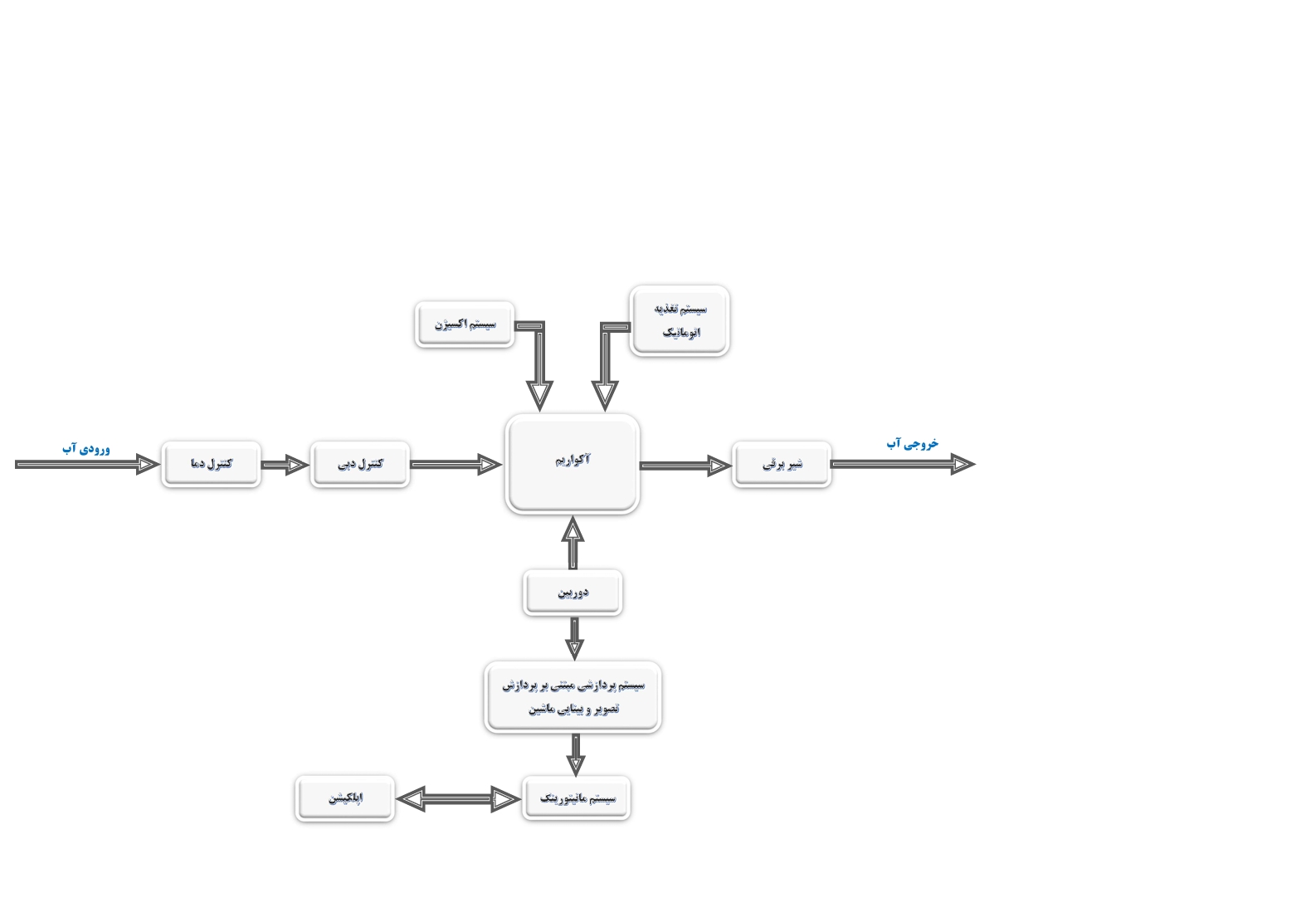
Key Components and Flow
-
Water Input and Filtration
Clean water enters the system through a controlled inlet and passes through multiple stages of mechanical, biological, and chemical filtration. This process mimics natural ecosystems, ensuring purity, protecting fish health, and supporting reliable system operation. -
Aquarium Core
At the center of the system is the aquarium that houses the zebrafish. It functions as the primary observation zone where behaviors are monitored under carefully controlled conditions. The setup includes a heater to regulate temperature and an aeration system to maintain oxygen levels, all fully automated through the ESP32 microcontroller. This controlled environment ensures stable living conditions while allowing precise behavioral monitoring. -
Monitoring and Control
A camera continuously records the aquarium, feeding data into machine vision algorithms that analyze fish movement, swimming speed, and behavioral patterns. The results are displayed through user-friendly software dashboards—showing trajectories, average speeds, and environmental parameters such as temperature, water flow, and oxygen levels. Sensors like the DS18B20 (for temperature) and YF-S201C (for flow) provide constant updates, ensuring quick and automatic adjustments whenever needed. -
Water Output
After circulation and monitoring, water exits through controlled valves and pumps, maintaining consistent flow and volume. This closed-loop design reduces waste and promotes sustainability. -
Additional Features
The schematic also includes auxiliary tools such as air pumps, digital displays, and interactive dashboards. These allow operators to visualize data in real time and receive alerts whenever potential pollutants are detected.
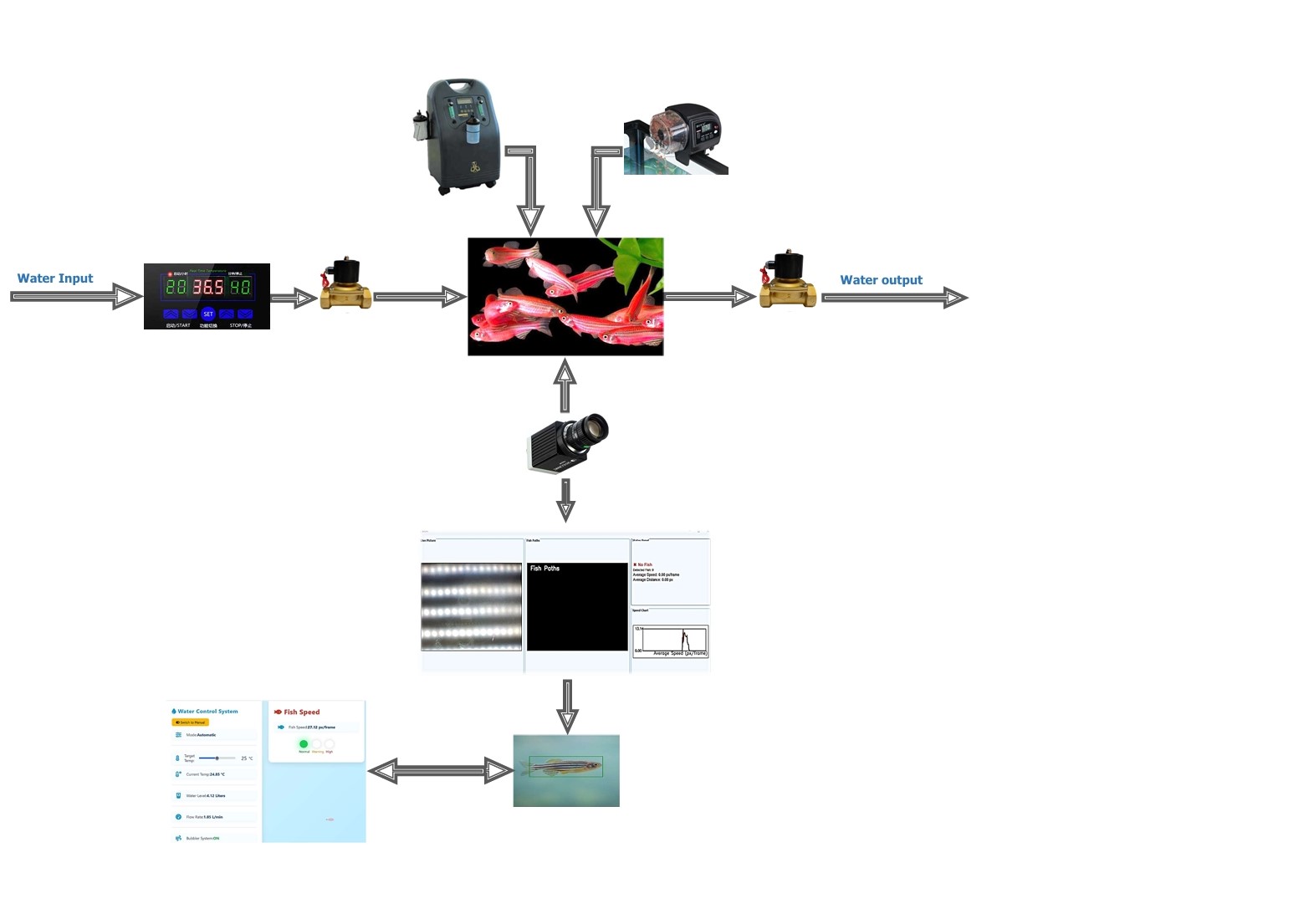
Why This Design Matters
Instead of focusing only on the hardware, the schematic presents a holistic picture of how BIOAI – AICER201 blends physical components with intelligent software. Its modular, visual design makes it easy to understand, whether you are a researcher, student, or industry professional.
-
Efficiency and Automation: Enables continuous, non-invasive biomonitoring without the need for manual intervention.
-
Adaptability: Scales from small research labs to larger aquaculture facilities.
-
Accessibility: Clear bilingual diagrams and simple visual flow make the system understandable even for non-experts.
Final Outcome
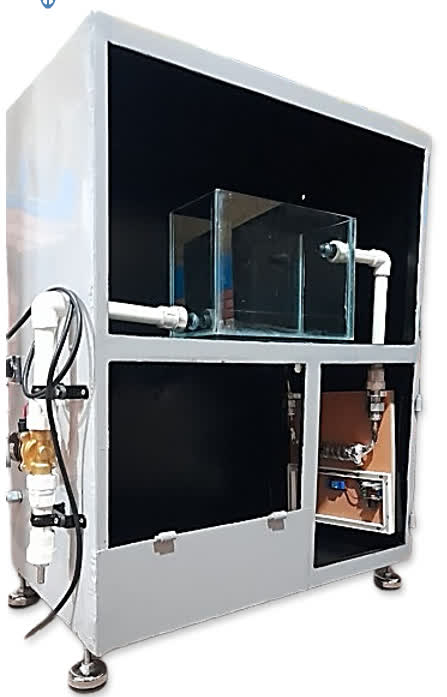
After months of design, development, and testing, all the individual components came together in this fully functional prototype of the BIOAI – AICER201 biomonitoring system.
This device represents more than just hardware: it is the practical realization of integrating biomonitoring, environmental control, and AI-powered image analysis into a single, reliable, and user-friendly platform. With its automated operation and real-time monitoring capabilities, the system is a step forward toward smarter, more sustainable solutions for water quality assessment.
What you see here is not only a product—it’s the embodiment of our vision at Aicer Lab: turning research into innovation that can make a real impact in science, education, and industry.


Developed and researched by Arvin Zaheri – Aicer Lab